USB, LAN, Wi-Fi or Handheld Oscilloscope?
Tech study | November 09, 2021
The variety of modern digital oscilloscopes used in automotive diagnostics makes choosing the right tool quite a difficult task. Therefore, it is good to get acquainted with the features of different types of oscilloscopes, their advantages and disadvantages, and here we will focus more on the interfaces for connection and data transfer between measuring devices and the personal computer.
COM and LPT
In the dawn of personal computers, the most used interfaces for communication with peripheral devices were the so-called Serial Port (Communication Port, COM) and Parallel Port (Line Printer Terminal, LPT). As their name suggests, through the serial interface, the bits flow sequentially, one after the other, while through the parallel port they are transmitted simultaneously. In the first case, we have fewer wires (COM uses a 9-pin connector), but the data transfer is slower, while in the second case the transfer is much faster, but the wires are more (LPT uses a 25-pin connector). What is important about this older communication technology is that these ports are connected directly to the CPU ports and operate on the interrupt architecture. What does this mean? Each time a digital edge, caused by a data packet waiting to be received or transmitted, appears at some CPU input, the CPU interrupts its work and processes the packet. Then returns to the location just before the interrupt and continues to follow instructions further. This functionality is provided by the hardware itself. That ensures the data are always transmitted and processed successfully. This type of communication is known for its trouble-free data transfer and lacks the so-colled hangs
that sometimes disrupt the operation of modern interfaces, such as USB or LAN.
The described architecture also has a significant drawback. The CPU is without protection against external influences through the pins of the serial and parallel ports. Only one touch on one of the ports with your hand is enough, and the accumulated static electricity (for example, from taking off your clothes or just rubbing your hand in your clothes) will permanently damage the computer. In those days, the personal computer was a much simpler device, so it didn't have as good protection as today's computers.

There are many examples of diagnostic oscilloscopes in the automotive industry, using data communication through the parallel port. These instruments are considered to be robust and reliable by many service professionals and are still used successfully in car diagnostics and maintenance.
USB
Due to the above-described shortcomings (and for many other reasons), some advanced and reliable interfaces have been developed over the years. The most used nowadays is the USB interface. It has become a standard in today's computers. Universal Serial Bus (USB) was developed in the late 1990s by an international group consisting of the world's largest manufacturers of hardware and software at the time. The purpose of the USB interface is to connect multiple external devices with the personal computer. It is based on the PCI interface and works as an abstract driver stack on top of the PCI driver. Many modern automotive digital oscilloscopes use the USB interface.
Advantages:
- High data transfer rate, up to 10 Gb/s.
- Few wires in the connecting cable (the interface is serial).
- Power supply to external devices via the communication cable. USB standard provides +5 V, 500 mA for each port.
- Short circuit protection.
- A robust and reliable connector allows multiple on/off switching cycles of the external device. The latter is very important when working in an industrial environment, as in the case of automotive oscilloscopes.
Disadvantages:
- The need for a special software driver to work with most types of peripherals. In the case of digital oscilloscopes used in modern automotive diagnostics, such a driver is mandatory.
- Limited cable length up to 5 m, and by the latest standards, the length is even shorter. The USB interface is essentially a voltage bus. Thus, in addition to the very high transfer rates, it is sensitive to external electromagnetic interference.
- Lack of built-in galvanic isolation. That requires special galvanic protection for each external device, when necessary. Our BOSA automotive oscilloscopes are an example of such protection. You can read more about BOSA's full internal isolation and technical parameters from the oscilloscope's hardware description page.
LAN
As the name suggests, Local Area Network, or LAN for short, is an interface designed to connect computers to a local area network, such as one in homes or office buildings. The most widely used LAN technology today is Ethernet. The widespread use of the LAN interface in today's computers makes its choice quite natural as a possible technology for communication between the personal computer and external devices.
Advantages:
- High transfer rate. For the most common standard at the moment (Fast Ethernet, IEEE 802.3u), it reaches 100 Mb/s and can reach up to 10 Gb/s (10 Gigabit Ethernet, IEEE 802.3ae). It is comparable to the one with the USB interface. That is quite understandable, given that both interfaces are modern and use the full capabilities of today's hardware. It's just that software architectures in their basics are fundamentally different.
- No need for special drivers to be installed. LAN interface is based on the TCP/IP architecture that rules the entire Internet. Thus, every modern operating system supports software TCP/IP driver stack that can be used directly by peripheral devices.
- Cable length up to 100 m. It is because the hardware is implemented as a current loop and is much more resistant to external electromagnetic interference.
- Built-in galvanic protection in the LAN connector.
Disadvantages:
- There is no power on the LAN cable. That requires additional hardware to power peripherals or batteries, whether rechargeable or disposable. As a result, we have complexity and an increase in the cost of the product.
- Low wear resistance connector, designed to work in a static environment. The thing is that the LAN interface is designed to make a connection between individual computers and not to operate with frequent plug-in/plug-out cycles. Therefore, it is not for constantly moving and vibrating devices, as in the case of automotive oscilloscopes used in service diagnostics.
- In the event of communication interrupt due to some interference, it takes longer for the peripheral device to restore its normal operation.

And one more thing. It is believed that the LAN interface, unlike USB, does not interrupt and does not allow the external device to hang
. That's not exactly right. Let us remind you again that Ethernet technology stands
in software terms on top of the TCP/IP architecture, which in turn drives the entire Internet. Thus, the TCP/IP protocol is very patient
when it comes to transmitting data packets. Its task is to find the amount of information requested by the end-user and provide it in full. For example, if you want to open a web page in your browser that is hosted on the other side of the world, TCP/IP technology is the one that takes responsibility for finding and delivering it to you so that you can view it on the screen. On its way to your computer or smartphone, the information passes through many other servers and routers, where all sorts of situations can occur that slow down the transmission of data packets. Even if all these components work perfectly in terms of hardware, slowdown or blocking the transmission can occur due to overloading the servers and routers with too many requests. Indeed, the Internet is a global network with huge sizes and an incredible amount of information stored in it!
TCP/IP technology is created with the intention to fight such problems. By default, it swallows
data transfer issues (so-called exceptions) and does not show a message on the screen. The protocol stays in waiting condition and tries to deliver the requested package. Do you remember how many times you were just staying in front of the screen, waiting for a page to appear in your browser? And this does not happen simply because there is a connection problem. Yes, at this moment, from the end user's point of view, all Ethernet technology is blocked, and there is nothing you can do. The same is true in the case of a peripheral device, such as a digital oscilloscope, using a LAN connection with the computer. If the connection fails, the data transfer stops, and the picture on the screen freezes
sometimes for a long enough time. Thus, only when the data transfer is restored, the measurement continues and the screen comes to life
again.
The case with the USB interface is different. The difference comes from the fact that USB is designed to connect peripherals that are physically close to the computer and most often connected directly to it. If a data transfer interruption occurs, it is most likely a signal of a hardware malfunction, not just an overload of the interface. An example is when we use a USB diagnostic oscilloscope to monitor the waveforms in the secondary ignition circuit of gasoline engines. Due to the high-frequency pulses in the measured signal, some interference can be induced, blocking the usual operation of the microcontroller, and hence the data transfer via USB. In this case, the reason is in hardware. That's why the USB interface raises an exception, and the user sees an error message on the screen. After starting the measurement again, the oscilloscope continues to operate normally.
The bigger problem is if the oscilloscope does not have galvanic isolation of the USB interface. High-frequency interference can then reach the computer and cause serious malfunctions that require a reboot of the operating system. To avoid such problems, BOSA car diagnostic oscilloscopes provide full galvanic isolation of the USB interface, both on data lines and on the power supply. Read more about the internal architecture of BOSA scopes.
Wi-Fi
In short, Wi-Fi is a wireless version of Ethernet technology. Okay, it's not exactly the same as Ethernet, but it does a similar job using electromagnetic waves instead of cables. With the mass usage of tablets and smartphones in our daily lives and the spread of the mobile internet, we have all become accustomed to the convenience of wireless devices and communications. Naturally, the use of Wi-Fi technology appears as one possible way of connecting peripheral devices to the computer, be it a desktop computer, laptop, smartphone, or tablet. Modern automotive oscilloscopes are no exception to this trend. Many manufacturers offer different types of diagnostic equipment using wireless technology.
Advantages:
- No connecting cables. Communication takes place via electromagnetic radio waves.
- Ability to connect to the peripheral device using a computer, tablet, or smartphone. Accordingly, greater flexibility in working with such equipment.
- Natural galvanic insulation.
Disadvantages:
- Slow transfer rate. Compared to wired Ethernet or USB, Wi-Fi communications are many times and even tens of times slower.
- The connection is unstable, interrupted, or sometimes even completely lost. It is susceptible to electromagnetic interference of any nature. That makes it very difficult to work with Wi-Fi devices in the industrial environment, as is the case with car repair shops.
- No power supply through the interface. And as with the LAN interface, this requires the use of additional power supply cables or batteries.
See the basic features and technical specifications of our automotive oscilloscopes.
Handheld oscilloscopes
In all the communication interfaces discussed so far, we have always talked about the connection between the peripheral device and the computer, whether it is a personal computer, laptop, tablet, or smartphone. There is also a separate class of diagnostic equipment. These are the so-called handheld devices, which are very common in the modern car service. They lack the computer, and most of its tasks are taken over by the device itself.
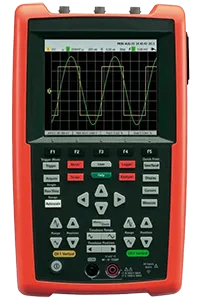
Advantages:
- There is no need for a computer and the associated costs.
- Easy and convenient operation. Handheld devices can be carried freely and used even in hard-to-reach places.
- There are no
hang
conditions specific to other communication interfaces.
Disadvantages:
- Hardware complication and increase in the final cost. Modern personal computers have computational power, a lot of memory and disk space, unbitable graphics capabilities, a user-friendly environment, operating systems, and standard input/output interfaces such as keyboard, mouse, or touch screen. And all this is missing in the case of handheld devices. Developers need to provide their substitutes. That is not an easy task and certainly significantly increases the cost of the device. Creating such equipment is often a compromise between the final price and the quality of the components being used. Typical examples are portable oscilloscopes with small, sometimes even monochrome displays with low resolution. Using such devices is not very comfortable, but unfortunately, these tools are quite common in today's automotive diagnostics.
- It is difficult to create a measurement database. Therefore, an additional interface to the SD card or USB flash drive is required to store the information recorded during the measurements.
- Need for an external power supply or internal rechargeable battery. In the latter case, the hardware is complicated due to the electronic subsystem controlling the battery charging process.
Despite the aforementioned disadvantages, handheld automotive oscilloscopes have a well-deserved place in modern vehicle diagnostic services and are well known among professionals in the industry.
The diversity of modern technologies makes the choice of diagnostic equipment a difficult process that requires careful approach and understanding. Good knowledge of computer interfaces and communication protocols is an important step to make easy taking the right decision in this choice.
Learn more about the capabilities, working modes and measuring settings of StudioBOSA automotive diagnostic software. On the library page you can read more about some of our interesting scientific works. Call us if you have more questions.