A New Portable 3D Magnetometer
Sci report | March 04, 2022
A new portable digital 3D magnetometer based on the anisotropic magnetoresistive (AMR) technology is developed. The compact design makes the instrument easy to use in both the laboratory and the field environment. Communication through a fast USB interface allows the use of μMeter in combination with different portable devices. Preliminary analysis of the measurement accuracy shows that the resolution of 2 nT with a sampling rate of 0.1 Hz is achievable.
Introduction
For the purposes of the weak magnetic fields measurements in the laboratory and the field environment, a compact and easy-to-use portable magnetometer is developed. μMeter is a digital 3D magnetometer measuring the magnitude and direction of the magnetic intensity simultaneously on the x, y and z axes. It is based on the HMC5883L integrated circuit of Honeywell International Inc and implements anisotropic magnetoresistive (AMR) sensor technology [1]. The device communicates to the PC via a USB interface, receives commands and sends the resulting measurement data. The data are displayed on the computer screen and saved on the hard disk for further processing and analysis.
Magnetometer basic scheme
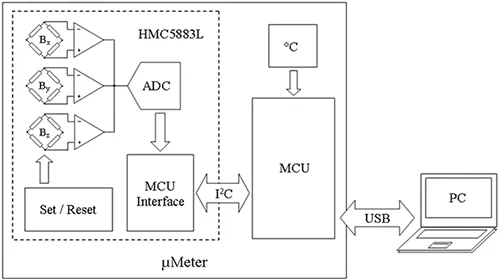
The device operation is controlled by a microcontroller with an integrated USB module that receives information from the computer containing the parameters of the current measurement, converts them into low-level commands, and sends them back to the HMC5883L chip via the standard I2C interface. After finishing the current measurement, HMC5883L sends the raw data packet to the MCU as 12-bit integer values. The microcontroller performs the primary data processing and measures the current temperature using an internal digital sensor. Finally, the MCU transfers data to the PC, where a GUI application is installed.
Software
The software is developed using C# for .NET Framework and works under MS Windows.
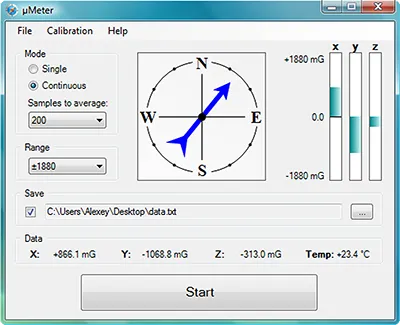
USB protocol is conformable to Human Interface Device (HID) standard. This is an important advantage, which eliminates the need for a special driver installation. HID devices use preinstalled drivers by default and are available in any modern operating system. The program sets the parameters of the magnetometer operation as range, averaging mode, single or continuous measurement. The resulting data are displayed numerically and graphically in real-time. The program allows acquired data to be written in a standard text file format with the user specified path on the system local hard drive.
Magnetic sensor internal structure
The magnetometer has eight measurement ranges from ±1 G to ±8 G [2]. The resolution for a single measurement (no averaging) in the most sensitive range reaches 500 μG (50 nT). Deviations in linearity are not to exceed 0.1 % in the full-scale of the given range. The data acquisition rate reaches 200 readings per second.
Internally, HMC5883L is a complex hybrid integrated circuit comprising several components: a sensor analog part and a subsystem to manage it, 12-bit ADC, MCU interface part responsible for communication with the microcontroller. The analog part consists of three separate (one for each axle) differential magneto-resistive bridges. Magneto-resistive elements are implemented as thin-film strips of nickel-iron ferromagnetic (Permalloy) material (similar to that used in the well-known magnetic tape recording) applied directly on the silicon substrate [1]. Initially, magnetic domains in each such element are oriented in the same direction and have a given conductivity so the bridge is balanced. When an external magnetic field is applied, domains reposition and thus change their resistance. As a consequence, the bridge becomes unbalanced. This change is amplified by a differential amplifier and is fed to the input of the internal 12-bit ADC. So the value of imbalance, which is a function of the external magnetic field, has been digitized. After each measuring cycle, the magnetic domains in the resistive elements need to be repositioned towards the initial zero direction. That is what the internal Set / Reset circuit is responsible for [3] [4]. It creates an artificial magnetic field by short electrical current pulses in both directions and thus, sets the domains in their zero direction. All this is packed into a tiny 3x3 mm plastic body, allowing the use of HMC5883L in applications with an extremely compact design.
First measurements
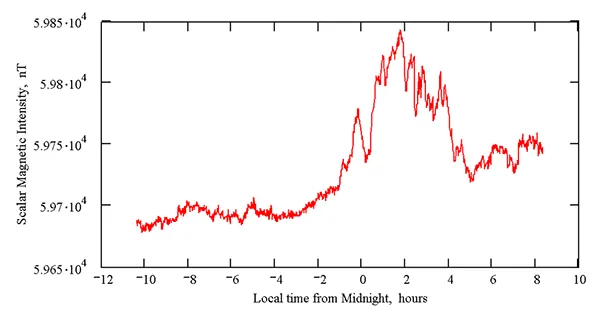
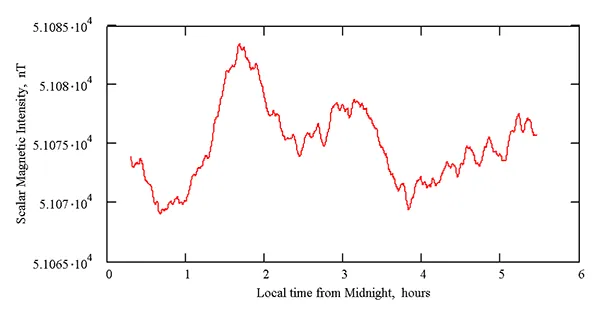
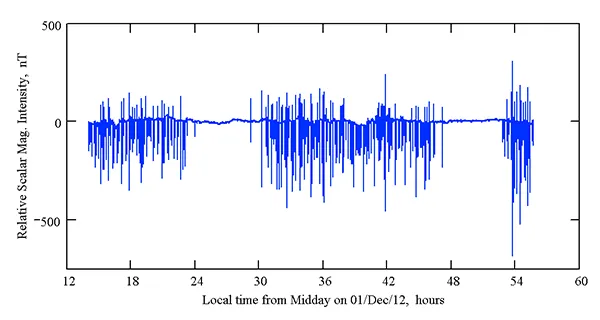
Conclusion
A new portable USB digital 3D magnetometer is developed. The compact design makes the device easy to use in laboratory and field environments. Communication via a fast USB interface allows for μMeter to be used with various modern portable devices such as tablets, smartphones, laptops. Preliminary analysis of the measurement accuracy shows that the resolution of 2 nT with a sampling rate of 0.1 Hz is achievable. μMeter is suitable for use in magnetic and geomagnetic studies and environmental monitoring. As a future work, we are intended to develop an accurate method for instrument calibration and provide a detailed study of the magnetometer's noise, its properties and spectral distribution.
Reference
- Caruso M., Bratland T., Smith C., Schneider R.
A New Perspective on Magnetic Field Sensing
, Sensors, December 1, 1998. - Honeywell.
HMC5883L Datasheet
, 2010. - Honeywell.
AN212 Handling of Sensor Bridge Offset
, Application Notes, 2010. - Honeywell.
AN215 Cross Axis Effect for AMR Magnetic Sensors
, Application Notes, 2010.
A preliminary version of this report was presented at the Eighth Scientific Conference with International Participation "Space, Ecology, Safety" December 04-06, 2012, Sofia, Bulgaria.